People spend 80%-90% of their time indoors, and indoor air quality is directly related to human health. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are typical air pollutants with strong toxicity in indoor environments. Among them, formaldehyde and benzene are a class of VOCs pollutants that are harmful to human health. Long-term exposure to formaldehyde and benzene can induce major diseases such as leukemia and lung cancer.
Source characteristics and risk assessment of VOCs pollution in indoor air are not comprehensive yet.
Recently, Prof. HUANG Yu’s research group from Institute of Earth Environment of Chinese Academy of Sciences, combining with VOCs on-site sampling and measurements, online gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, source apportionment, and questionnaires, etc., had systematically investigated on the source characteristics and emission concentration of VOCs in indoor air in different areas of Xi'an and had made some results.
They had found that the higher concentrations of VOCs were acetone, formaldehyde, naphthalene, and methylene chloride in the indoor environment in Xi'an. Indoor insecticides, bleaches, detergents, decoration materials and furniture were the main emission sources.
Among them, formaldehyde was the most important indoor toxic VOCs. Although its emission concentration was lower than the national indoor air quality standard (100 μg·m-3), long-term exposure still posed a greater risk to human health.
Decoration materials and furniture contributed approximately 44.5% to the concentration of VOCs, 11.9% for paints and adhesives, 17.3% for detergents, 9.8% for cooking sources, and 14.5% for smoking, respectively.
Based on the standard calculation method of human health risk assessment by US Environmental Protection Agency VOCs, it was concluded that formaldehyde, 1,3-butadiene and 1,2-dichloroethane were the three VOC pollutants with the highest cancer risk.
This work has deepened the understanding of the characteristics, sources and health risks of VOCs in the indoor environment of western China, and will provide strategy recommendation to the causes analyzing of indoor air pollution and the formulation of control measuresin China.
This work has been published in Science of The Total Environment.
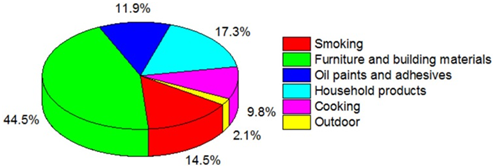
Fig. 1.Source apportionment of indoor VOCs in Xi'an in winter.(Imaged by HUANG, Yu et.al )
Contact: Bai Jie, Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi'an, China. Email: baijie@ieecas.cn
 © 2015 Institute of Earth Environment,CAS
© 2015 Institute of Earth Environment,CAS Address:No. 97 Yanxiang Road, Xi'an 710061, Shaanxi, China

 Location :
Location :