Rising Summer Maximum Temperature Influence Climate Warming: Insights from Tree-ring Evidence
As one of the regions most affected by global climate warming, the Tianshan Mountains has experienced several ecological crises, including retreating glaciers and water deficits. Climate warming in these mountains is considered mainly to be caused by increases in minimum temperatures and winter temperatures, while the influence of maximum temperatures is unclear.
A research team led by Prof. LIU Yu from the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences used a 300-year tree-ring chronology developed from the Western Tianshan Mountains to reconstruct the summer (June–August) maximum temperature (Tmax6-8) variations from 1718 to 2017.
The reconstruction explained 53.1% of the variance in the observed Tmax6-8. Over the past 300 years, the Tmax6-8 reconstruction showed clear interannual and decadal variabilities. There was a significant warming trend (0.18℃/decade) after the 1950s, which was close to the increasing rates of the minimum and mean temperatures. The increase in maximum temperature was also present over the whole Tianshan Mountains and its impact on climate warming has increased. The Tmax6-8 variations in the Western Tianshan Mountains were influenced by frequent volcanic eruptions combined with the influence of solar activity and the summer North Atlantic Oscillation (SNAO).
This study reveals that climate warming is significantly influenced by the increase in maximum temperatures and clarifies possible driving mechanisms of temperature variations in the Western Tianshan Mountains which should aid climate predictions.
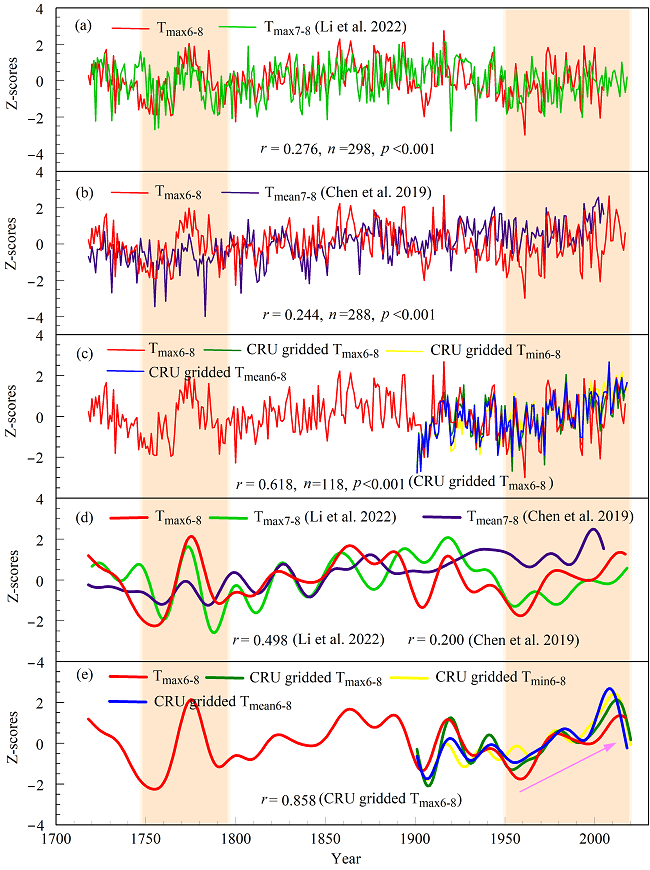
Fig. 1 Comparisons between our reconstructed Tmax6-8 series and nearby temperature series. (a) Tree-ring density-based Tmax7-8 reconstruction in the southern Tianshan Mountains (Li et al. 2022); (b) tree-ring density-based Tmean7-8 reconstruction in the Tianshan Mountains (Chen et al. 2019); (c) CRU TS4.03 gridded temperature data; (d) the 20-year low-pass filtering of nearby temperature series; (e) CRU TS4.03 gridded temperature data after 20-year low-pass filtering. Correlation coefficients are shown. (Image by REN Meng)
This work published in Journal of Forestry Research, was funded by the 2nd Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research, the China Desert Meteorological Science Research Foundation, the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, CAS.
Contact: BAI Jie, Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi'an, China. Email: baijie@ieecas.cn
 © 2015 Institute of Earth Environment,CAS
© 2015 Institute of Earth Environment,CAS Address:No. 97 Yanxiang Road, Xi'an 710061, Shaanxi, China

 Location :
Location :